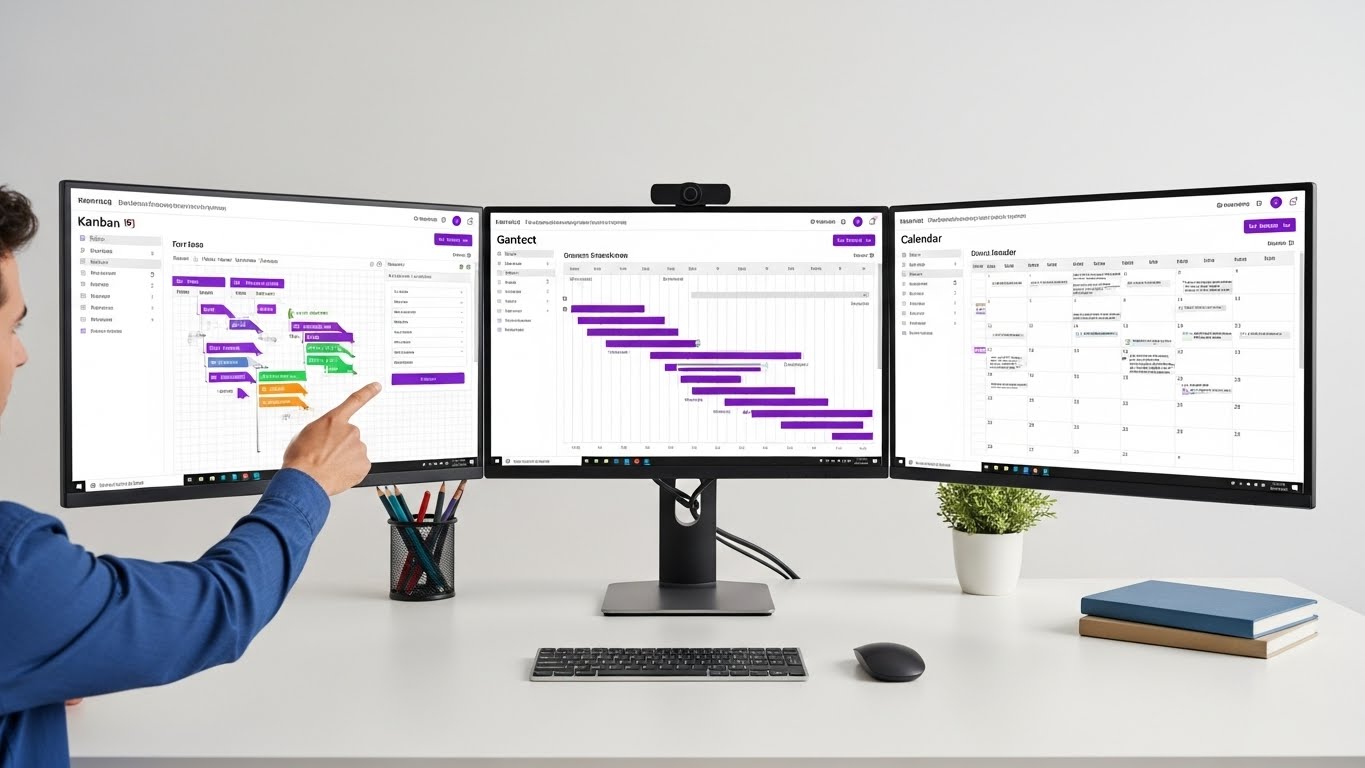
The way you visualize your work fundamentally shapes how you manage it. A task buried in a long list feels different than the same task prominently displayed on a Kanban board. A project timeline viewed in a spreadsheet conveys different information than the same timeline rendered as a Gantt chart.
Most project management software offers only one view option-typically a board. But modern teams need more flexibility. Different project phases, team roles, and work types demand different visualizations. That's why Protawk offers 3 distinct project views, each designed for specific use cases.
This guide explores each view, when to use it, and how to combine views for maximum productivity.
Why View Flexibility Matters
Before diving into specific views, let's understand why having multiple options matters.
Different Roles Need Different Views
Consider a software development team:
- Developers want to see their assigned tasks and current sprint work
- Project managers need to track timeline dependencies and resource allocation
- Designers prefer visual organization of design tasks by project phase
- Executives want high-level status without granular details
- Clients need simplified progress views without internal complexity
One view can't serve all these needs effectively. When tools force everyone into the same visualization, some roles suffer.
Different Project Phases Need Different Views
Projects evolve through phases, each with different information needs:
- Planning phase: Need to brainstorm, organize ideas, see the big picture
- Execution phase: Need to track daily work, manage workflow states
- Timeline management: Need to visualize dependencies and deadlines
- Review phase: Need to organize deliverables and track approvals
- Reporting phase: Need to aggregate data and communicate status
A Kanban board excels during execution but fails during timeline planning. A Gantt chart handles timelines but obscures daily task management. Multiple views let you use the right tool for each phase.
Different Work Types Need Different Views
Even within a single team, work types vary:
- Recurring tasks benefit from calendar views
- Sequential workflows suit Kanban boards
- Complex projects require Gantt charts
- Data-heavy work needs table views
- Creative work benefits from visual organization
Trying to force all work types into one view creates friction and reduces visibility.
View 1: Kanban Board
The Kanban board is perhaps the most popular project view, and for good reason. It provides intuitive workflow visualization that anyone can understand in seconds.
How It Works
Tasks are represented as cards arranged in columns. Each column represents a workflow stage: To Do, In Progress, Review, Done (or whatever stages fit your process). Moving tasks between columns shows progress through the workflow.
When to Use Kanban
Workflow-based work: When tasks flow through defined stages, Kanban makes that flow visible. Software development, content creation, and design projects all benefit.
Daily task management: For understanding what's being worked on right now, Kanban provides instant clarity. What's in progress? What's stuck in review? What's waiting to start?
Team workload visibility: Seeing who has cards in their column reveals workload distribution. Too many cards in one column indicates bottlenecks.
WIP limits: Kanban supports Work In Progress limits-caps on how many items can be in a column simultaneously. This prevents overload and encourages finishing before starting.
Kanban Best Practices
Keep columns meaningful: Each column should represent a distinct state. If items frequently skip columns or the distinctions are unclear, reorganize.
Limit WIP: Set maximum items per column to prevent overload. Start conservative (3-5 items) and adjust based on experience.
Use swimlanes: Horizontal lanes can separate work by project, priority, or assignee, adding another dimension to organization.
Regular grooming: Periodically review the board to archive completed items, update stale cards, and ensure accuracy.
Kanban in Protawk
Protawk's Kanban includes:
- Drag-and-drop card movement
- Customizable column names and colors
- WIP limits per column
- Swimlane grouping options
- Quick-add cards to any column
- Card details expansion without leaving the board
View 2: Gantt Chart
Gantt charts are the gold standard for timeline and dependency management. They show when tasks happen, how long they take, and how they relate to each other.
How It Works
Tasks appear as horizontal bars on a timeline. The bar's position shows start date; its length shows duration. Lines connecting bars indicate dependencies-which tasks must complete before others can begin.
When to Use Gantt
Timeline planning: When you need to see how a project unfolds over time, Gantt provides clarity no other view matches.
Dependency tracking: Understanding which tasks block others is crucial for complex projects. Gantt charts make dependencies visual.
Resource allocation: Seeing who's working on what and when reveals conflicts and overallocation.
Deadline management: When multiple deadlines interact, Gantt charts show how delays cascade through the project.
Client communication: For showing project timeline to stakeholders, Gantt charts communicate professionally.
Gantt Best Practices
Right zoom level: Most Gantt tools offer day, week, month, and year views. Use the zoom that shows appropriate detail without overwhelming.
Meaningful dependencies: Only create dependencies that genuinely exist. Artificial dependencies create false constraints.
Include milestones: Mark major checkpoints distinctly from regular tasks. Milestones anchor the timeline.
Regular updates: Gantt charts only help if they're current. Update task progress and dates as the project evolves.
Gantt in Protawk
Protawk's Gantt includes:
- Multiple zoom levels (day, week, month, year)
- Drag-and-drop date adjustment
- Click-and-drag dependency creation
- Milestone markers
- Today indicator
- Critical path highlighting
- Baseline comparison
- Export to image or PDF
View 3: Calendar View
The calendar view places tasks on a familiar calendar interface, organized by date. It's ideal for deadline-driven work and scheduled activities.
How It Works
Tasks with due dates appear on the calendar at their deadline date. Tasks with both start and due dates span across days. Monthly, weekly, and daily views offer different perspectives.
When to Use Calendar
Deadline management: When due dates are the primary organizing principle, calendar view keeps them front and center.
Recurring work: Weekly meetings, monthly reports, and regular deliverables are naturally suited to calendar organization.
Time-sensitive projects: Event management, content publishing, and marketing campaigns with specific dates benefit from calendar visualization.
Personal planning: For individual task management, many people think in terms of "what's due this week?"
Client deliverables: When clients expect deliverables on specific dates, calendar view ensures nothing slips.
Calendar Best Practices
Don't overload dates: Too many items on one day becomes unreadable. If dates are crowded, some work should shift.
Use color coding: Different colors for different project types, priorities, or team members add information density.
Combine with other views: Calendar shows when; Kanban shows status. Use both for complete visibility.
Regular review: Weekly calendar reviews prevent deadline surprises.
Calendar in Protawk
Protawk's Calendar includes:
- Month, week, and day views
- Drag-and-drop rescheduling
- Multi-calendar support
- Color coding by project or category
- Quick task creation on any date
- iCal sync for external calendar integration
Combining Views for Maximum Effectiveness
Individual views are powerful, but the real magic happens when you combine them strategically.
Planning Phase
Use Gantt to create the timeline and identify dependencies. See the big picture of your project phases and milestones.
Execution Phase
Work primarily in Kanban for daily task management. Check Calendar for upcoming deadlines.
Client Communication
Share Gantt views for timeline visibility. Use Calendar for deliverable deadlines.
Choosing Your Primary View
While flexibility is powerful, you'll likely have a primary view you use most often. Choose based on your work style:
If you think in workflows: Kanban is your home If you think in timelines: Gantt is your home If you think in deadlines: Calendar is your home
Start with your natural fit, then expand to other views as situations demand.
Why 3 Views Beats 1
Most project management software offers only a board view-sometimes adding timeline as a premium feature. Protawk's 3 views represent a fundamental difference in philosophy:
Flexibility over rigidity: Your tool should adapt to you, not vice versa.
Role accommodation: Different team members can use views that fit their needs while staying in sync.
Phase appropriateness: Use the right view for each project phase without switching tools.
Complete coverage: From brainstorming to reporting, every phase has an appropriate view.
Competitive advantage: View flexibility that competitors hide behind expensive plans is available to all Protawk users.
Experience All 3 Views Today
The best way to understand Protawk's view flexibility is to experience it firsthand. Create a project and try each view. See how the same data appears differently across visualizations. Discover which views fit your workflow.
All 3 views (Kanban, Gantt, Calendar) are available in Protawk's free tier-no upgrade required to access Gantt charts or any other view. See why view flexibility is the feature teams didn't know they needed until they had it.
Great work happens when your tools adapt to you. Protawk's 3 project views ensure you always have the right visualization for the job.